When it comes to security challenges, businesses often believe that simply updating their antivirus will keep them safe from ransomware.
But in the unforgiving world of cyber threats, this strategy falls disappointingly short, resulting in lost data, time, and money.
Understanding ransomware and adopting the right techniques and best practices to combat it is key. Let’s chart the path.
Understanding Ransomware and How It Works
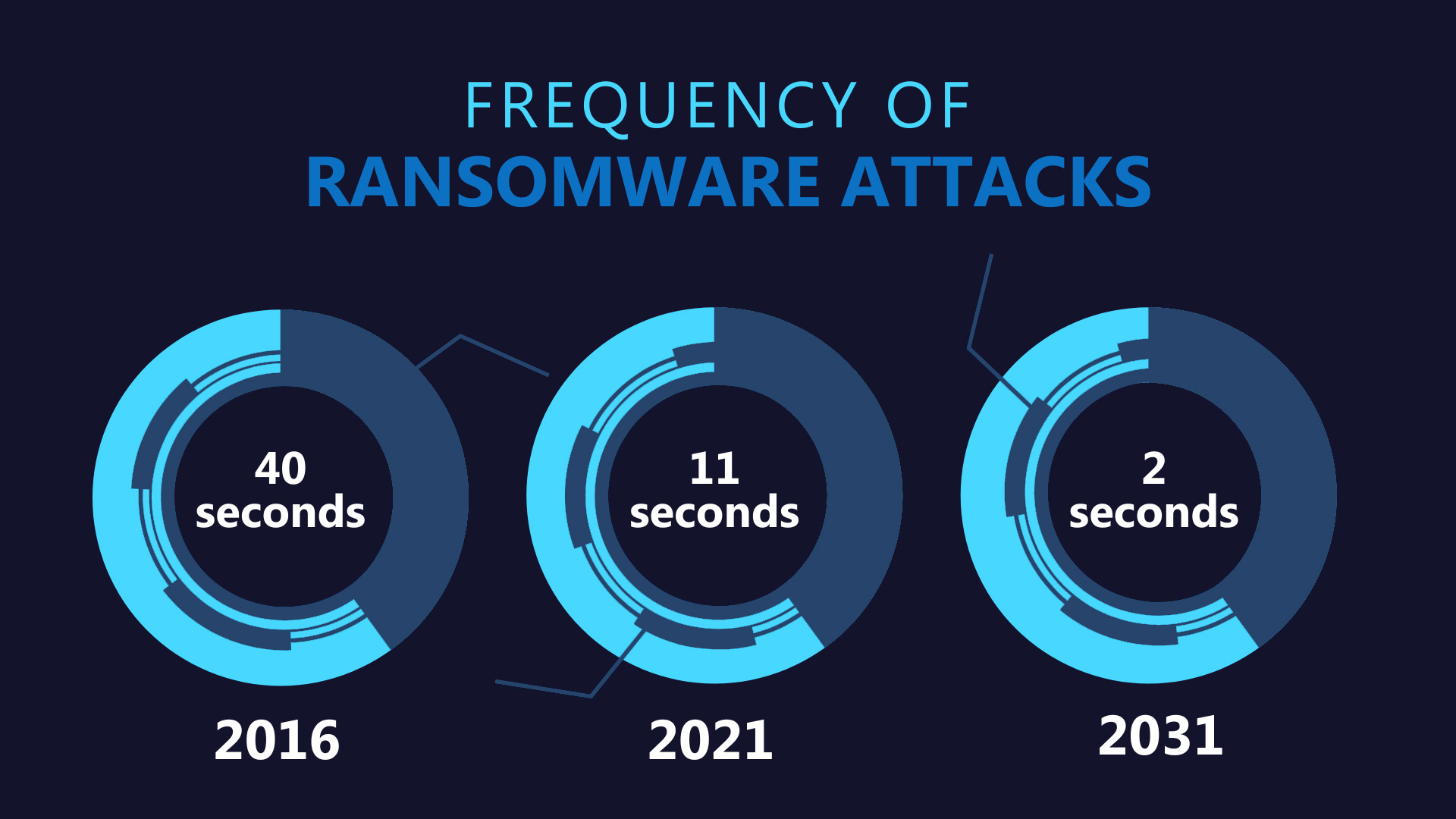
Businesses have been concerned for some time about the abundance and gravity of ransomware attacks. Cybercriminals have infiltrated and are targeting every industry, and it’s predicted that ransomware will cost its victims around $265 billion annually by 2031. This is a massive leap from the estimated $1 billion it cost businesses in 2016. The percentage of businesses hit by ransomware attacks worldwide has also steadily increased since 2018, reaching a peak of 71% in 2022.
Understanding ransomware means recognizing potential targets and weak spots, knowing when they might be vulnerable, and understanding the common threats that can occur. It’s also important to understand the financial impact of these attacks, the technologies that can prevent them, and what happens after a breach.
This knowledge is key in building a strong defense against the constantly changing cybersecurity landscape.
Ransomware, a form of malicious software, encrypts files and demands payment for their release – a digital shakedown, if you will. Cybercriminals use this tactic to block data or system access, typically through encryption, with the victim’s access only restored upon paying a ransom.
The infection can occur via:
- email attachments
- external storage devices harboring the malware
- compromised websites, or
- network service vulnerabilities.
When activated, the ransomware either locks the computer screen or encrypts specific files (known as crypto-ransomware).
In the first instance, an image or message pops up on your screen, effectively barricading access to your system while providing instructions for ransom payment. Alternatively, the ransomware may target critical files such as documents or spreadsheets, restricting access until the ransom is paid.
Often, these payments are demanded in untraceable virtual currencies like Bitcoin, keeping the cybercriminal’s identity concealed. Stay vigilant and safeguard your digital assets. Here are 7 best practices to get you started.
7 Best Practices for Ransomware Protection
Regularly back up your on-premise and cloud data
Keep all systems and software updated
Install antivirus software and configure your firewall
Implement network segmentation
Educate end-users
Use intrusion detection systems
Create an incident management response plan
Ransomware attacks can devastate your business, your reputation and your customers. Fortunately, there are a number of best practices that can help you prevent and mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks. Here are some of the most important ones:
1. Regularly back up your on-premise and cloud data
Follow the 3-2-1 rule by keeping at least three separate versions of data on two different storage types with at least one offsite is the most effective way to handle ransomware attacks.
Cloud Provider Resiliency (CPR)™, for example, offers secure replication and storage of both public and private cloud data and virtual machines, guaranteeing recovery from disruptions. If cloud data becomes inaccessible, the service can restore it, malware-free, to its original provider or temporarily to a private cloud until the original environment is restored.
2. Keep all systems and software updated
Outdated software and systems often have known vulnerabilities that can be exploited by ransomware. This seems like a no-brainer, yet research shows that 60% of breaches occur due to an unpatched known vulnerability. By regularly updating your software and operating systems, you can substantially reduce your risk of a successful ransomware attack.
3. Install antivirus software and configure your firewall
Comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware software can go a long way to defend against ransomware. They can scan, detect, and respond to cyber threats. However, you’ll also need to configure your firewall since antivirus software only works at the internal level and can only detect the attack once it is already in the system.
Closely related is filtering your emails by either disabling file execution in e-mail attachments or quarantining all attachments using your spam filter.
4. Implement network segmentation
Network segmentation mitigates ransomware spread by dividing the network into isolated segments, each with unique security controls and firewalls. This strategy not only prevents the disruption of network services and widespread infection but also buys time for threat identification and removal.
5. Educate end-users
The human factor has long been identified as the weakest link in data breaches and one of the top drivers of ransomware attacks succeeding. In fact, human error is the root cause of 82% of data breaches, which makes this a very important best practice to adhere to.
Regularly train your employees on how to identify and avoid common ransomware pitfalls such as malvertisements, phishing emails, and so on. This can be done through:
- regular security training;
- real-world simulations; and
- tabletop exercises
to help employees recognize and report suspicious behavior.
6. Use intrusion detection systems
Cut off ransomware attacks at the knees by using continuous monitoring to detect signs of anomalous or malicious activity in real time.
You can automate this process by using threat detection software that uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data and detect anomalous behavior, such as unusual access patterns or data exfiltration attempts.
7. Create an incident management response plan
This should not just be some document gathering dust in your drawer or saved somewhere on your hard drive. Treat it as a living document and update it regularly with:
- security best practices;
- key contacts; and
- security procedures
so you and your team are ready in case a security incident is encountered. The idea is to be prepared and ready for any kind of disruptive event or eventuality.
Cloud Service Providers + Incident Response + Disaster Recovery = Your First and Last Lines of Defense Against Ransomware
Understanding cyber threats isn’t just about knowing the risks. It’s about emergency preparedness and having the right tools in place.
In this area, cloud service providers have emerged as a vital ally in ransomware prevention and protection. Harnessing the power of cloud technology, cloud service providers can offer comprehensive data security measures to safeguard your digital assets.
One of the key advantages of using cloud services lies in its robust data protection and recovery capabilities. Cloud storage ensures that your data is not only securely stored but also easily retrievable, providing an essential safety net in the event of a ransomware attack.
Moreover, a well-crafted disaster recovery plan and the right security tools can significantly mitigate and even prevent the impacts of ransomware attacks. By regularly backing up data to the cloud and implementing rapid recovery protocols, businesses can minimize downtime and swiftly restore business operations.
Case Study: Copperfin Credit Union
Final Thoughts
A ransomware protection strategy is no longer just an option but a necessity for businesses. A single ransomware attack can cripple operations, compromise sensitive data, and tarnish the hard-earned reputation of your enterprise.
Ransomware, a malicious software, encrypts critical files and systems, holding them hostage until a ransom is paid. Not only does this result in financial loss, but the downtime and recovery process can also lead to significant operational disruptions.
That’s why robust ransomware protection measures, such as advanced threat detection, secure cloud backups, employee training, and incident response plans, are so important. By proactively safeguarding your digital infrastructure, you fortify your business against cyber threats, ensuring continuity, customer trust, and overall business resilience.
Don’t wait for disaster to strike—take action now.





