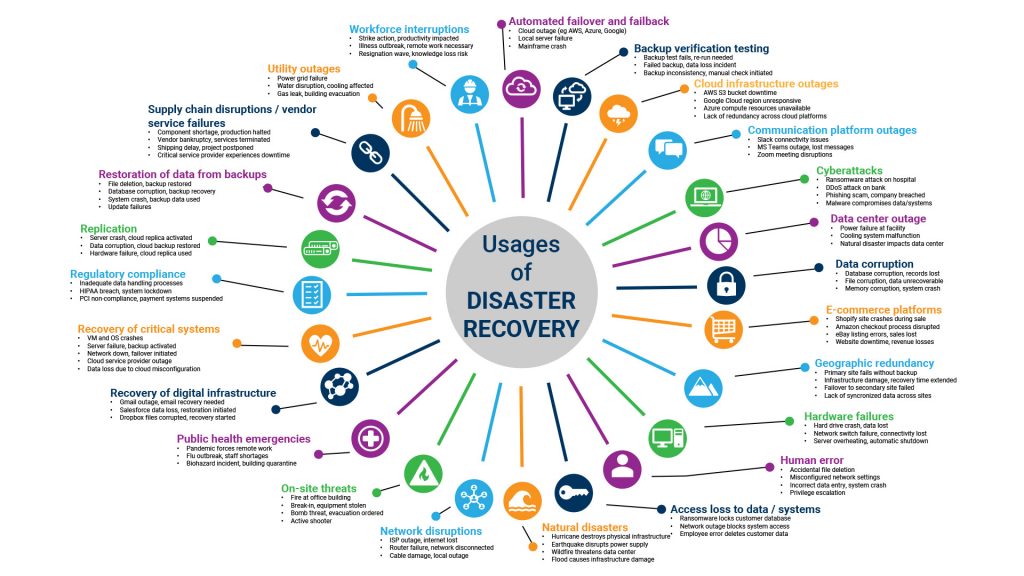
In today’s world, considering disaster recovery as an optional add-on is not just naïve but perilous. Unexpected disasters strike indiscriminately, leaving unprepared businesses to bear the brunt.
Disaster recovery is more than just a safety net for your business; it’s a strategic approach to ensure uninterrupted operations and maintain customer trust even in the face of unforeseen events. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into 24 diverse use cases where a robust disaster recovery solution can save the day.
1. Automated failover and failback
Two key components have become critical for maintaining business continuity: automated failover and failback.
Automated failover is the process where systems automatically switch to a standby or backup system when the primary system fails. This ensures uninterrupted service and data availability even in the face of unexpected system failures.
Automated failback refers to the automatic restoration of systems and applications back to their original state once the primary system has been fixed or restored.
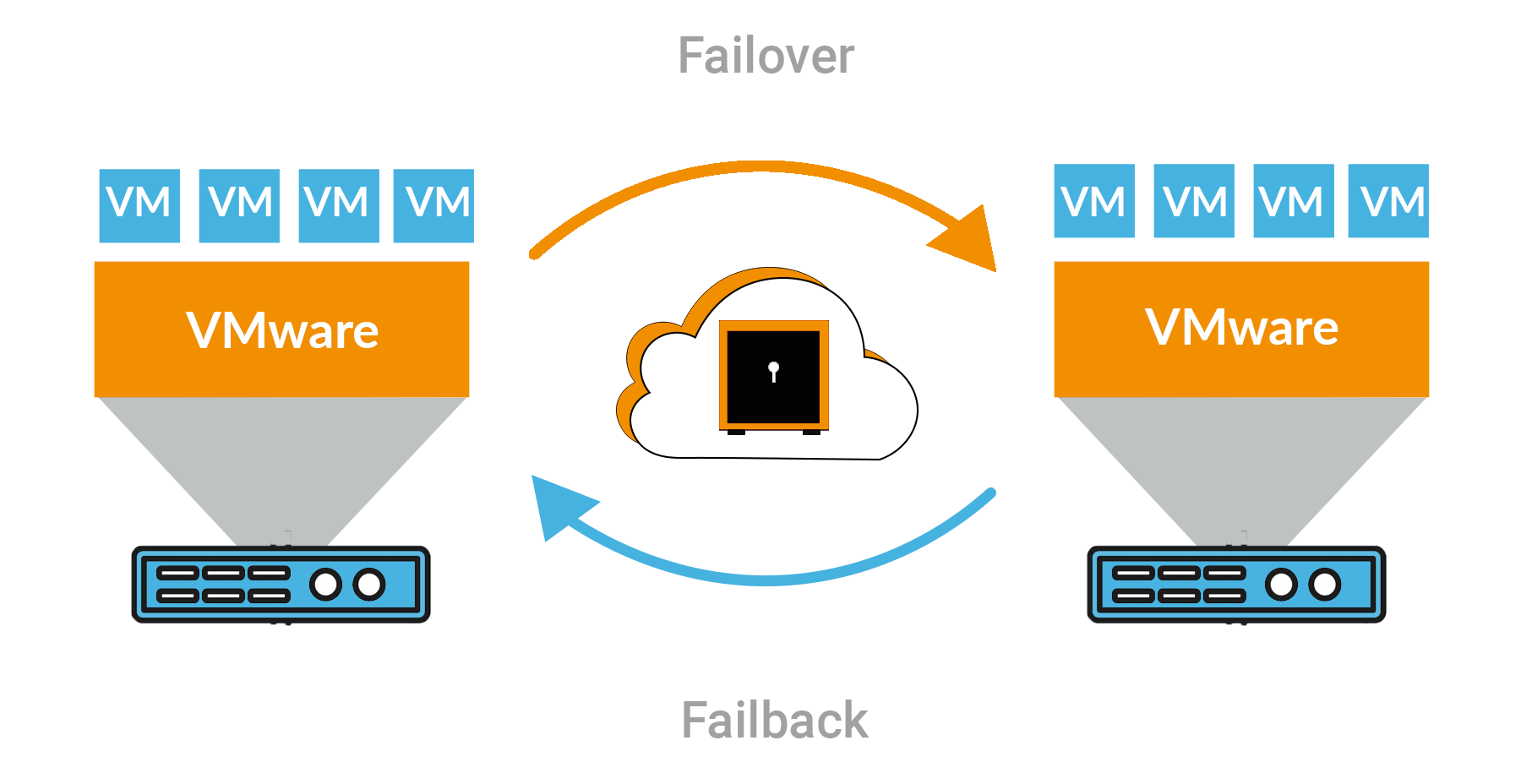
These processes are crucial for business continuity as they minimize downtime, maintain data integrity, and ensure seamless operations during unforeseen events such as:
- Cloud Outages: In the event of a cloud outage, automated failover kicks in, transferring your operations to a backup cloud environment. This ensures that your business continues to operate smoothly despite the temporary unavailability of your primary cloud platform.
- Local Server Failures: When a local server fails, automated failover quickly switches your operations to a redundant server. This swift transfer prevents data loss and keeps your services online, minimizing the potential impact on your business.
- Mainframe Crash: Mainframes are the backbone of many businesses, storing critical data. A crash can be catastrophic. However, with automated failover, your operations are instantly transferred to a standby system, ensuring your data remains accessible and your business functional.
2. Backup verification testing
Backup verification testing is a crucial step in data protection. It involves routinely checking your backups to ensure they’re reliable and can be restored when needed. This process is vital because it uncovers potential issues, such as corruption or incomplete backup before a data loss event occurs. Here are the steps:
- Identify Key Backups: Figure out which backups are crucial based on their relevance and usage frequency.
- Pick Your Backup Method: Choose a backup technique that matches your company’s requirements.
- Craft a Backup Testing Strategy: Build a plan detailing when and how backups will be tested.
- Perform Full Restoration Tests: Regularly test full restorations, especially for critical data, to catch potential hardware or software issues.
- Check Backup Integrity: Use checksums to confirm your backups’ reliability and usability against the original data.
- Test Recovery Steps: Ensure your recovery process is efficient, timely, and compatible with your systems.
- Verify Database Recovery: Restore your database to a cloud-based virtual machine and run tests for verification.
- Time Your Backups: Track how long backups take to ensure they fit within your schedule.
- Test Remotely: Try out your backup and recovery strategy remotely for a real-world scenario test.
- Regular Testing: Keep testing your backup and recovery plan routinely to maintain its effectiveness.

3. Cloud infrastructure outages
How much data can you afford to lose?
Cloud infrastructure outages can happen, and the costs can be significant, with an estimated cost of $365,000 per hour of downtime for businesses.
The effective disaster recovery plan for cloud infrastructure failures is a comprehensive strategy that prioritizes proactive measures to minimize downtime, data loss, and business disruptions. The components of a robust disaster recovery plan should include:
- Backup and restore: Regularly back up your data to an off-site location so you will be able to restore it from the backup in the event of a disaster.
- Replication: Create a duplicate copy of your data in a different location to help minimize downtime in the event of a disaster.
- Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service: This is a cloud-based service that provides a complete disaster recovery solution and is ideal for businesses that cannot manage their own disaster recovery solution.
4. Communication platform outages
According to a recent survey, 65% of businesses reported experiencing at least one instance of communication platform downtime in the past year.
During communication platform outages, teams may experience delays in sending and receiving messages, leading to communication breakdowns. This could result in missed deadlines, confusion, and a decrease in overall productivity.
5. Cyberattacks
Disaster recovery plans help businesses maintain business continuity after a cyber-attack. Disaster recovery plans can be applied to both natural disasters and cyberattacks.
A disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) provider can move a business’s computer processing to its own cloud infrastructure. This allows the business to continue operations even if its servers are down. They can help businesses:
- restore access to compromised systems
- recover critical systems and data
- reduce business downtime
- prevent further damage
- reduce recovery costs
- improve compliance
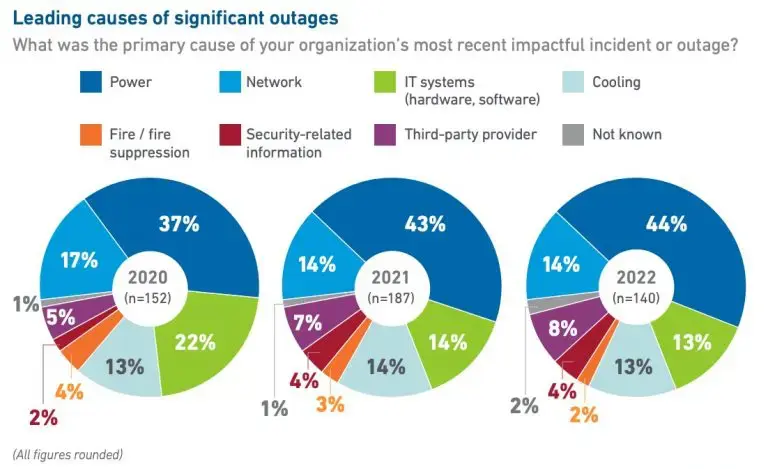
6. Data center outage
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses rely heavily on data centers to keep their operations running smoothly. However, even the most advanced facilities can experience unexpected outages that disrupt services and impact revenue streams.
Unplanned downtime is a data center operator’s worst nightmare. In 2023, 70% of outages cost a minimum of $100,000, with 25% costing over $1 million. The top three culprits were: Power failures, cooling system failures, and natural disasters. A robust disaster recovery plan can counter these outages:
- Power Failures: Use robust backup systems like UPS to avoid business downtime due to power outages.
- Cooling System Failures: Regular maintenance and backup cooling systems help prevent equipment damage and potential fire hazards.
- Natural Disasters: Incorporate disaster-resistant design, redundant sites, and cloud-based backups to safeguard data centers from natural disasters.
7. Data corruption
Most people think securing their data means just having a good antivirus. It’s a decent start, but there’s more lurking beneath the surface.
Data corruption, whether in databases, files, or memory, can be devastating, often leading to significant loss of data, irretrievable files, and even total system crashes.
Our advice? Implement a robust cloud security and disaster recovery strategy.
- Backup your data regularly and store it in a safe location.
- Use transactions and logging to validate and sanitize your data before inserting or updating it in your database.
- Have a recovery plan in case something goes wrong.
- Conduct an asset inventory and perform a risk assessment.
- Define your recovery objectives and goals.
- Involve your business stakeholders in the disaster recovery planning process.
- Document and test your disaster recovery plan
Continuous data replication can also help protect against some types of disaster and will provide maximum protection if it also includes versioning of stored data or options for point-in-time recovery.

8. E-commerce platforms
E-commerce platforms are the lifeblood of modern retail, enabling businesses to reach customers globally. However, with great opportunity comes great risk.
Imagine the chaos if a Shopify site crashes during a peak sale period, the Amazon checkout process grinds to a halt, or eBay listings are plagued with errors, causing potential sales to slip away. Even a few minutes of website downtime can lead to substantial revenue losses and irreparable damage to your brand’s reputation.
Having an effective disaster recovery plan can help e-commerce platforms ensure business continuity, minimize data loss and reduce the risk of permanent damage to their business. It can also help them remain cost-efficient and maintain maximum operational efficiency in the event of a crisis

9. Geographic redundancy
High availability geo-redundancy is the practice of distributing mission-critical components or infrastructures, such as servers, across multiple data centers that reside in different geographic locations.
This is an ideal solution in the following scenarios:
- Primary site fails without backup
- Infrastructure damage, recovery time extended
- Failover to secondary site failed
- Lack of synchronized data across sites
Overall, geo-redundancy is an important part of disaster recovery planning and can help organizations ensure high availability and resilience of their IT infrastructure and data in the face of unexpected events.
10.Hardware failures
Hardware failures strike without warning, disrupting operations and jeopardizing sensitive data. Whether it’s a
- hard drive crash causing data loss
- a network switch failure leading to connectivity issues
- or a server overheating and triggering automatic shutdown
the impact can be severe. Here are some tips on how to develop a disaster recovery strategy to prevent data loss from hardware failures:
- Begin with a business continuity plan that includes a disaster recovery plan.
- Back up your data regularly and store it in a safe location.
- Replicate data to the cloud to ensure availability and accessibility.
- Set recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO) to ensure that your recovery plan meets your business needs.
- Continually monitor device performance and replace aging hardware before it fails.
- Regularly update and patch systems to eliminate vulnerabilities that could lead to system failure.
- Develop a recovery procedure in the event of a disaster that includes identifying alternate suppliers who can provide critical systems such as hardware, power, networking, and replacement components.
By implementing these tips, organizations can minimize the risk of data loss from hardware failures and ensure business continuity in the event of an outage or disaster

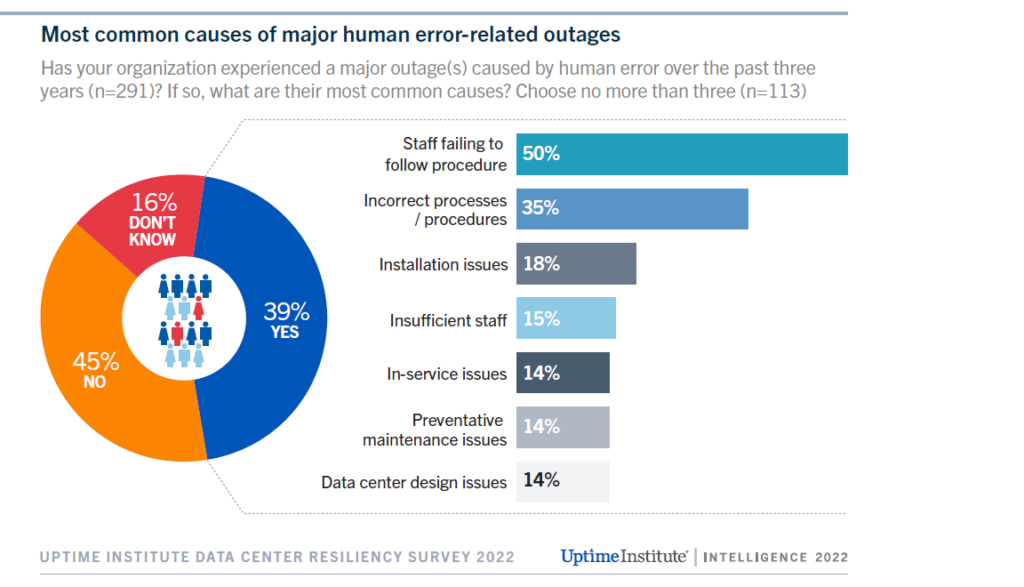
11. Human error
The assumption that your staff will always follow cybersecurity best practices is a gamble.
The common barrier is the human factor; the lack of proper training and awareness can lead to breaches, costing the company significant losses. In fact, human error is responsible for the vast majority of data breaches and cybersecurity problems. The numbers don’t lie:
- Accidental file deletion – 75%
- Misconfigured network settings – 44%
- Incorrect data entry – 75%
- Privilege escalation – 20%
- Data entry, with no verification layer steps – 4%
- Lack of training – 50%
- Social engineering – 47%
- Insider threats – 60%
Moreover, research by the Uptime Institute estimates that human error plays a role in about two-thirds of all outages.
Disaster recovery can help prevent human errors in a number of ways:
- Employee Training: Teach your employees the importance of data protection with a disaster recovery plan that includes employee training. This will help them understand how to avoid common mistakes that can lead to data loss.
- Limiting Access: A disaster recovery plan can also limit employee access to sensitive systems, reducing the risk of accidental data loss.
- Customized Strategies: Each organization has different needs and risks, so a disaster recovery plan can help you develop a strategy specifically tailored to your business to prevent human error.
- Regular Testing: Test your disaster recovery plan regularly to identify potential issues before they cause problems. This will ensure that your plan is effective in preventing data loss from human error.
- Stronger File Access Controls: A disaster recovery plan can include establishing stronger file access controls to prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of accidental data loss.
- Automated Backups: With automated backups, replication, off-site verification, and restoration processes, you can reduce the risk of human error by eliminating the need for manual intervention.
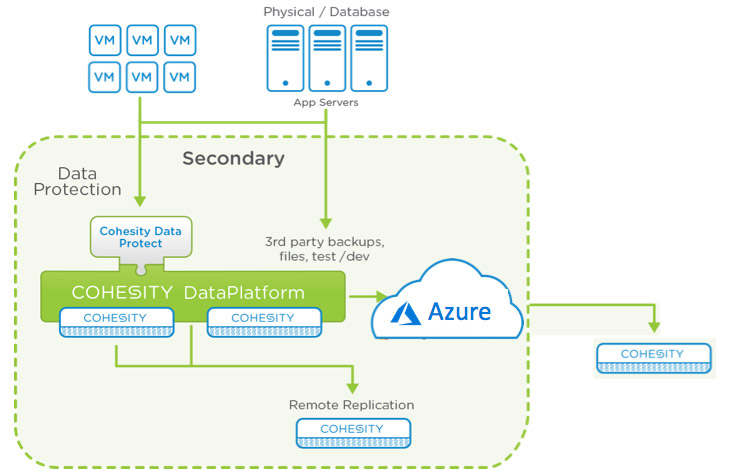
12. Access loss to data/systems
Access loss to data and systems can be a nightmare for any business. Whether it’s ransomware locking your customer database, a network outage blocking system access, or an employee inadvertently deleting valuable customer data, the consequences can be severe.
A disaster recovery strategy that includes Helios can protect against data loss and loss of access to systems through:
- Backup and Recovery: Helios provides modern, software-defined backup and recovery that protects all data sources, simplifies backups and ensures instant recovery while reducing costs.
- Long-Term Retention and Archival: Cohesity’s cloud-native solution simplifies long-term data and application retention, supporting backup and archival of data directly to Stage2Data’s private cloud.
- File and Object: Consolidate files and objects easily at scale with Cohesity’s global deduplication, search, multiprotocol access, unlimited scalability, and public cloud integration.
- Cloud Data Management and Protection: Cohesity’s scalable and pay-as-you-go solution natively integrates with Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, making it ideal for multiple use cases, from data backup to disaster recovery.

13. Natural disasters
Imagine running a business and waking up one day to find that a natural disaster has wiped out all your critical data. That’s a nightmare scenario for many business owners, especially when you consider these startling statistics:
- Almost half (40%) of small to mid-sized enterprises don’t survive such events and never reopen their doors.
- 2021 was a record year for climate disasters. There were 20 events, each causing over $1 billion in damages.
- Hurricanes are particularly destructive, causing power failures, flooding, loss of customers, and forcing many businesses to close.
But it doesn’t have to be this grim. Disaster recovery strategies are designed to mitigate the impact of data loss due to natural disasters. Here’s how they can help:
- A well-structured disaster recovery plan can dramatically cut downtime and minimize data loss.
- These plans offer robust protection against data loss, ensuring your business can bounce back after a disaster.
- With a disaster recovery plan in place, your operations can continue with minimal interruptions.
- Perhaps most importantly, these plans are designed to restore operations as quickly and efficiently as possible, getting your business back on its feet in no time.
In essence, while natural disasters can wreak havoc on businesses, causing significant data loss, a solid disaster recovery plan can be your shield. It ensures minimal downtime, reduces data loss, keeps operations going, and restores operations swiftly and efficiently. Plus, it offers the necessary protection against data loss.
14. Network disruptions
In our hyperconnected world, network disruptions can bring business operations to a grinding halt. From ISP outages to router failures and cable damage, these network-related disasters emphasize the need for a seamless disaster recovery plan that makes provision for the often-neglected networking portion of your system.
To create an effective network disaster recovery plan, you should list the steps to restore network connectivity, identify critical network components, create a recovery team, backup network configurations, and test the plan. Adding Network Recovery-as-a-Service to your disaster recovery strategy allows for zero modification during failovers, preserving all internal and external IP addresses and keeping entire networks intact.

15. On-site threats
Disasters aren’t limited to just your digital data or your cloud infrastructure; they can manifest physically as well. On-site threats like fires, break-ins, bomb threats, and active shooter situations can pose immense danger to both personnel and critical assets.
This is where a disaster recovery plan comes into play. It’s like a roadmap that guides you through these challenging events, helping your business come out the other side intact and operational. Here’s how:
- Physical Security Measures: The plan outlines all physical security measures to protect information and assets.
- Identifying Critical Assets: The plan prioritizes restoring critical assets to minimize downtime.
- Creating a Recovery Team: The plan designates a team with specific roles for handling crises.
- Backing Up Data: The plan ensures data is backed up and can be restored quickly.
- Testing the Plan: Regular testing is done to confirm the plan’s effectiveness and readiness.
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan can be your business’s lifeline during a physical security threat. It’s about safeguarding your physical security measures, restoring critical assets, creating a competent recovery team, backing up data, and testing the plan to ensure it works when needed. It’s not just about surviving the disaster; it’s about coming out stronger on the other side.
16. Public health emergencies
Navigating the rapidly changing landscape of global threats highlights that disaster recovery planning has never been more important.
From pandemics to biohazard incidents, businesses are facing unprecedented challenges. In this age of remote work, flu outbreaks, and potential building quarantines, a robust, adaptable disaster recovery plan is not just an option – it’s a necessity.
A disaster recovery plan should include pandemic recovery tools and guidelines, identify critical assets, create a recovery team, backup data, plan for recovery from a biological incident, and develop recovery plans before a public health emergency strikes.
17. Recovery of digital infrastructure
In an era where every piece of data matters, imagine this: your team logs into Gmail one morning only to find an unexpected outage. Your inboxes are inaccessible, and critical emails are lost in the ether.

Or picture your Salesforce platform suffering from data loss and vital customer information missing at the click of a button. Perhaps even your Dropbox files, the backbone of your collaborative projects, have become corrupted and unreadable.
That’s why you need a disaster recovery plan. It can help with the recovery of digital infrastructure by identifying critical systems and networks, creating a recovery team, backing up data, testing the plan, and including pandemic recovery tools and guidelines.
18. Recovery of critical systems
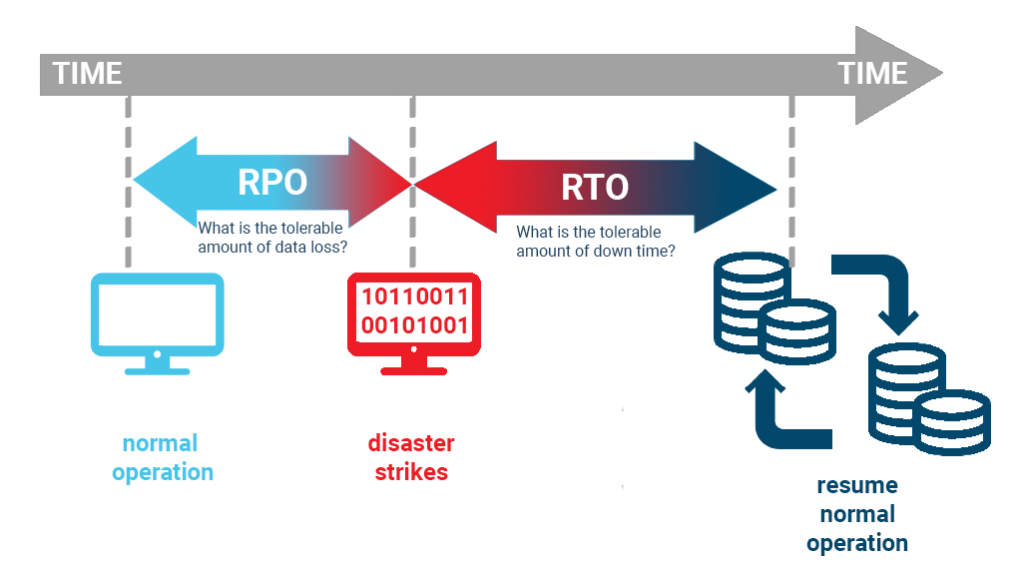
In our tech-driven world, challenges like VM and OS crashes, server failures, network issues, or cloud service provider outages are inevitable. Misconfigurations can even lead to data loss. That’s where understanding RPOs and RTOs comes in.
RPO, or Recovery Point Objective, is all about data. It’s the maximum age of files that an organization must recover from backup storage for normal operations to resume after a disaster. So, if your RPO is 2 hours, then backups need to be performed every 2 hours.
On the other hand, RTO is about time — it’s the duration of time within which a business process must be restored after a disaster in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity.
For instance, when a server goes down, you need a plan to get your backup up and running quickly. Similarly, if your network takes a hit, you need to have a failover ready to jump in. In the face of a cloud service provider outage or data loss due to cloud misconfiguration, your disaster recovery plan should switch on without missing a beat.
By using these strategies and including an RTO and RPO as part of your disaster recovery strategy, you’re setting your business up to weather any storm. In our field, being proactive isn’t just smart – it’s essential.
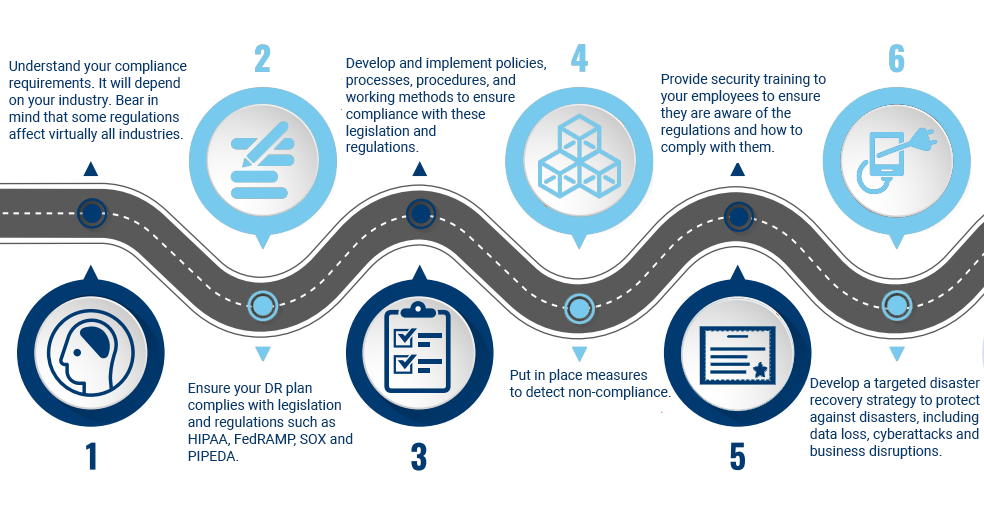
19. Regulatory compliance
Disaster recovery compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes — it’s about making sure your business is ready and able to bounce back from any disaster. It means setting up reliable data backup, crafting a solid disaster recovery plan, and regularly testing your recovery procedures to make sure they’re up to scratch.
Mishandling data can lead to some serious headaches for businesses. Let’s break down a few potential outcomes:
PCI Non-Compliance:
- Fines: If you’re not upholding payment security, payment processors and credit card companies can slap you with fines ranging from $5,000 to $10,000 a month. They do this to offset the potential losses they face due to your lack of security.
- Increased risk of data breaches: Not complying with PCI DSS can leave you more exposed to data breaches. This could put your customers’ financial and personal data at risk.
- Suspended payment systems: If you’re found to be non-compliant with PCI DSS, your payment systems could be suspended. This could seriously impact your day-to-day business operations.
HIPAA Breach:
- Sanctions and penalties: Non-compliance with the HIPAA Privacy Rule can result in sanctions and penalties. Even during a national or public health emergency, this rule isn’t suspended.
- Lawsuits: If you violate HIPAA regulations, you could be hit with lawsuits from consumers for negligence and damages.
- System lockdown: In case of a HIPAA breach, your systems might need to be locked down to stop further unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Don’t let your organization be caught off guard. Prioritize data-handling processes to avoid these consequences. Make sure you’re complying with regulations such as PCI DSS and HIPAA Privacy Rule, put security measures like firewalls and data encryption in place, and conduct regular risk assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Remember, other regulations like the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), and Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) are also important to consider. In this digital age, being proactive about data security isn’t just smart—it’s essential.
20. Replication
Replication is a key technology for disaster recovery, and it can help with the recovery of digital infrastructure in various ways:
- Server Crash: Imagine your server crashes — with replication, you’ve got a backup plan. You can activate a cloud replica, an exact copy of your original server. This replica steps in, restoring your data and applications so your business can keep running smoothly.
- Data Corruption: If your data gets corrupted, you can restore from your cloud backup, a trustworthy version of your data. It’s like having a digital rewind button to get back all your functions in case of a mishap.
- Hardware Failure: If your hardware fails, you can turn to your cloud replica. Again, it’s an exact copy of your original hardware and can step in as a failover site, keeping your operations up and running.
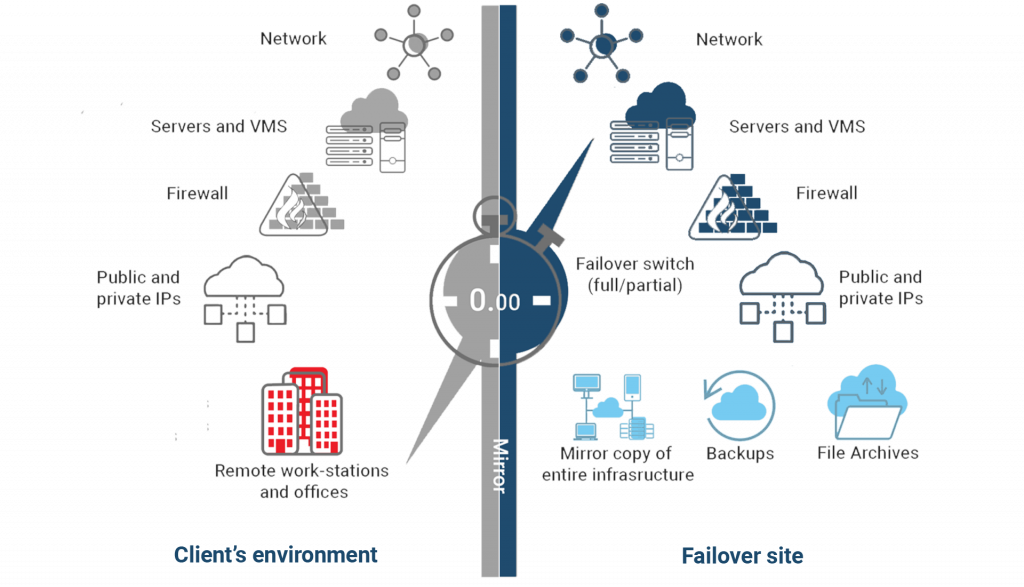
21. Restoration of data from backups
Restoring data from these backups often proves to be a monumental hurdle, riddled with time-consuming tasks and technical challenges.
Backups are only one component of a disaster recovery solution, and they are not enough to ensure business continuity if you experience a region-wide outage or large-scale cyberattack.
A proper disaster recovery plan gives you a comprehensive strategy for responding to a disaster event or disruption and puts the backups into action. It also identifies critical systems and networks, creates a recovery team, backs up data, and tests the plan.
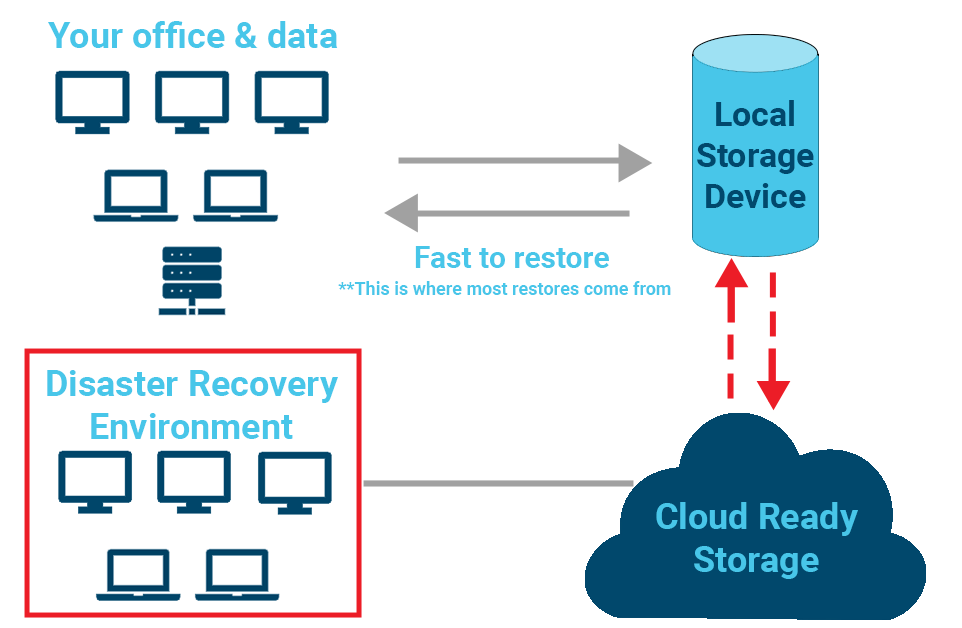
22. Supply chain disruptions/ vendor service failures
A single vendor failure can cause significant interruptions to your business operations, especially if you’re heavily reliant on that vendor for critical inputs. If your suppliers don’t have a solid disaster recovery plan, this could lead to massive disruptions in your own supply chain
According to a Deloitte case study, 80 of respondents have suffered a supply disruption in the last 12-18 months.
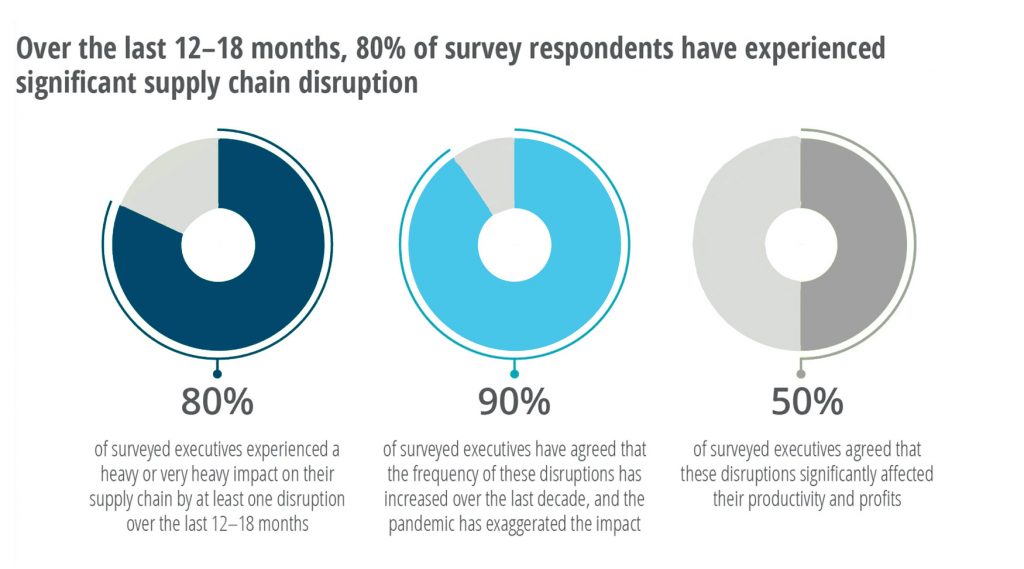
So, how do you shield your operations from such risks?
The first step is to identify your key suppliers and evaluate the likelihood of any disruption or failure in the supply chain. You also need to have backup plans ready for any potential technological failures or incidents within your supply chain. A well-crafted disaster recovery plan can help you navigate these disruptions, ensuring a smooth flow of supply.
But what if a critical third-party vendor lacks a robust business continuity plan? It’s essential to understand their concept of business interruptions and failures, their documented RTOs, and their action plan for such scenarios.
Supply chain continuity planning isn’t just about reacting to incidents—it’s about preparing for them. It involves creating a practical framework to manage incidents, recurring supplier failures, customer service hiccups, and tech failures due to upgrades. You should have mitigation strategies and measures ready in case of dependencies failing, catastrophic disasters, or when providers of critical materials or services stumble.
Keep in mind a disruption in your supplier chain can trigger natural hazards, power outages, transportation failures, and a host of other unforeseen events. A supply chain failure can have severe consequences for your company, including lost revenue, decreased customer satisfaction, and a hit on your reputation.
23. Utility outages
The power grid is the backbone of modern society, powering everything from our homes to our businesses. But as recent headlines show, it’s under increasing strain. From supply and demand issues exacerbated by droughts to the disastrous power crises of 2021 and 2023, it’s clear that power grid failures are becoming a pressing concern.
Water disruptions and gas leaks add further complexity to this issue. A water disruption can affect cooling systems, vital for maintaining optimal temperatures in data centers and other tech-heavy environments. A gas leak could necessitate building evacuation, leading to significant operational downtime.
This is how a disaster recovery strategy can help:
- Power Grid Failure: Your disaster recovery plan should include provisions for alternate power sources such as generators or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to keep critical systems operational during a power outage.
- Water Disruption: If cooling systems fail due to water disruption, having a contingency plan for alternative cooling methods or backup data centers can be a lifesaver. Ensuring your data is backed up and can be quickly restored in a secondary location allows for business continuity even in the event of a major disruption.
- Gas Leak: In the event of a gas leak and subsequent building evacuation, a good disaster recovery plan should include remote work capabilities. This ensures that even if physical access to an office or data center is not possible, work can still continue. Cloud-based backups and applications play a key role here.
24. Workforce interruptions
In our rapidly evolving work environment, unexpected disruptions can have significant impacts on productivity. Let’s delve into three potential scenarios: strike actions, illness outbreaks, and a wave of resignations. Each presents unique challenges, but with a well-structured disaster recovery plan, your business can weather these storms.
- Strike Actions: Recent data indicates a nearly 50% increase in major strike activity in 2022, which can significantly impact productivity. Strikes can cause ripple effects across industries, particularly if they involve critical sectors such as the auto industry. A robust disaster recovery plan should include strategies for managing labor disputes and maintaining operations during strikes. This might involve developing relationships with temporary staffing agencies, cross-training employees to fill in for striking workers, or investing in automation to reduce dependency on human labor.
- Illness Outbreaks: The COVID-19 pandemic has shown us that illness outbreaks can necessitate remote work. In response, a disaster recovery plan should incorporate a comprehensive remote work strategy. This includes cloud-based backups and applications to ensure employees can access necessary systems and data from anywhere. It also means investing in secure, reliable technology infrastructure to support remote work and regularly testing these systems to ensure they’re ready when needed.
- Resignation Wave: With the ongoing Great Resignation, businesses face the risk of significant knowledge loss. Your disaster recovery plan should include knowledge management strategies to capture and retain critical institutional knowledge. This could involve creating detailed process documentation, investing in training and cross-training, and implementing knowledge-sharing platforms.

Final Thoughts
Acts of nature, malicious attempts to disrupt operations, and equipment failure are just a few of the scenarios that threaten business data and operations. By anticipating these potential disruptions and preparing for them with a comprehensive disaster recovery plan, your business can maintain continuity and resilience, no matter what challenges arise.
Investing in a disaster recovery solution today can give your company the capability to protect itself against any kind of scenario, however unlikely.